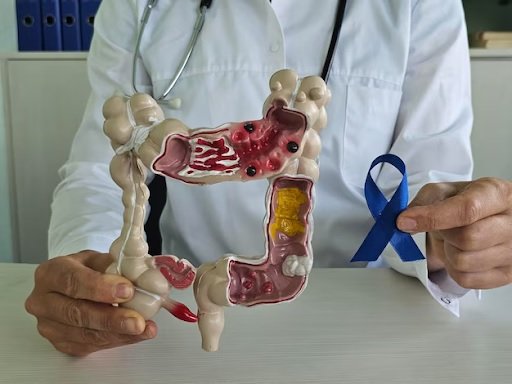
Colon cancer, a type of cancer that begins in the large intestine, typically develops over time from precancerous growths known as polyps. These polyps often go unnoticed in the early stages as they do not present obvious symptoms. However, as cancer progresses, more pronounced signs may emerge, which are essential to recognise for early intervention. Understanding colon cancer, its symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures is vital for improving survival rates and managing the disease more effectively.
Colon cancer is one of the most common forms of cancer worldwide, but it is also one of the most preventable cancers if detected early. The awareness of risk factors, symptoms, and screening methods plays a critical role in reducing the incidence and mortality associated with colon cancer. With proper knowledge, individuals can take proactive steps towards their health, recognise the warning signs early, and consult healthcare providers for necessary screenings and preventive measures.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Colon Cancer
Colon cancer can develop slowly over time without causing any noticeable symptoms in the early stages. This is why regular screenings, such as colonoscopies, are crucial, particularly for individuals aged 50 and above or those with a family history of the disease. As the cancer progresses, however, various signs may emerge that serve as warning signals. These symptoms can include changes in bowel habits, such as diarrhea, constipation or a feeling that the bowel does not empty. Another common symptom is the presence of blood in the stool, which may be visible or detectable only through lab tests. Additionally, unexplained weight loss, persistent abdominal pain, cramping or bloating may occur, signalling potential underlying issues that require further evaluation.
When these symptoms arise, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis. To confirm the presence of colon cancer, a series of tests are typically performed. These tests may include a colonoscopy, where a flexible tube with a camera is inserted into the colon to view any abnormalities, as well as biopsy procedures to collect tissue samples for laboratory analysis. Other diagnostic tools may involve imaging tests, such as CT scans, which help to determine the spread of the cancer to nearby organs.
Early detection is key in managing colon cancer effectively. In the early stages, treatment options are more likely to be successful, and the chances of complete remission are higher. Regular screenings can help detect the disease before symptoms even appear, significantly improving the odds of successful treatment.
Treatment Options for Colon Cancer
The treatment for colon cancer largely depends on the stage of the disease, the size and location of the tumour, as well as the overall health of the patient. If the cancer is detected early and confined to the colon, surgical removal of the tumour is often the first line of treatment. During a procedure called a colectomy, a surgeon removes the cancerous portion of the colon, along with some healthy tissue surrounding the tumour to ensure all cancer cells are removed. If the cancer is localized and has not spread, surgery alone can often cure the disease.
In cases where the cancer has spread beyond the colon to nearby lymph nodes or distant organs, additional treatments may be necessary. Chemotherapy is a common treatment option that uses drugs to kill cancer cells or stop their growth. Chemotherapy is often used after surgery to reduce the risk of recurrence. Radiation therapy may also be employed to target and destroy cancer cells, especially in cancers located in the rectum or other areas that may not be accessible to surgery alone.
In more advanced stages, when colon cancer has metastasized to other parts of the body, targeted therapy or immunotherapy may be used. These treatments work by targeting specific proteins or genetic mutations in cancer cells, helping to slow or stop the spread of the disease. Immunotherapy, which boosts the body’s immune system to fight cancer, has shown promising results for some patients with advanced colon cancer.
Treatment plans are highly individualized, and oncologists typically tailor therapies based on the patient’s unique situation. Supportive care, such as pain management and nutritional support, is also an essential component of treatment, aiming to improve the patient’s quality of life during the recovery process.
Prevention Strategies for Colon Cancer
While colon cancer is a serious health concern, there are several strategies that individuals can adopt to reduce their risk of developing the disease. These prevention measures are especially important for people with a family history of colon cancer or those who are at higher risk due to other factors, such as age, lifestyle, or genetic predispositions.
One of the most effective preventive measures is regular screening. Colonoscopies are recommended for individuals over the age of 50 or earlier if there is a family history of colon cancer or certain inherited conditions. Colonoscopies help identify polyps before they have the chance to develop into cancer, enabling their removal during the procedure. Early detection is essential because it allows for treatment before cancer has the chance to spread.
In addition to screenings, maintaining a healthy lifestyle is another key preventive measure. A diet high in fibre, fruits, and vegetables and low in red meats and processed foods, has been shown to reduce the risk of colon cancer. Regular physical activity can also lower the risk, as being active helps maintain a healthy weight and improves overall digestive health. Obesity is a known risk factor for colon cancer, so staying at a healthy weight is important.
Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption and quitting smoking are additional preventive measures that can significantly reduce the risk of developing colon cancer. Both smoking and excessive drinking are linked to an increased likelihood of colorectal cancer, as they contribute to the development of mutations in the cells of the colon.
Some individuals, particularly those with a family history of colon cancer, may benefit from genetic counselling to assess their risk and consider options like genetic testing. For those who are at an increased genetic risk, additional screening measures or preventive treatments may be recommended.
Colon Cancer FAQs
What is the life expectancy of a person with colon cancer?
The life expectancy of someone diagnosed with colon cancer can vary depending on factors such as the cancer’s stage at diagnosis, the patient’s overall health, the effectiveness of treatments, and adherence to post-treatment care. Early-stage colon cancer has a much better prognosis than late-stage cancer, and many patients live for years after successful treatment.
Can colon cancer be cured?
Yes, colon cancer can often be cured, particularly if it is detected early. Surgery to remove the cancerous tissue, combined with chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy, can lead to full remission in many cases. The earlier the cancer is diagnosed, the higher the chances of a successful cure.
What are the first warning signs of colon cancer?
Some early warning signs of colon cancer may include changes in bowel habits, such as persistent diarrhea or constipation, blood in the stool, unexplained weight loss, and abdominal discomfort or bloating. These symptoms can be indicative of various health issues, so it is important to consult a doctor if they persist.
How fast does colon cancer spread?
The rate at which colon cancer spreads varies depending on individual factors such as the tumour’s location, genetic factors, and overall health. If left untreated, colon cancer can spread to nearby lymph nodes and other organs, but early detection can significantly slow its progression and improve outcomes.
Colon cancer is a serious health issue, but with early detection, appropriate treatment and preventive measures, the chances of a successful outcome can be significantly improved. Regular screenings, a healthy lifestyle, and being aware of the potential symptoms of colon cancer are crucial for reducing the risk and ensuring timely intervention. If you experience any concerning symptoms or are at higher risk due to family history or lifestyle factors, consult a healthcare professional to discuss your options for prevention and early detection.